Find Nearest Retailer!
Notified by email when this product becomes available

- Description
- Downloads
RUG INSIGHT
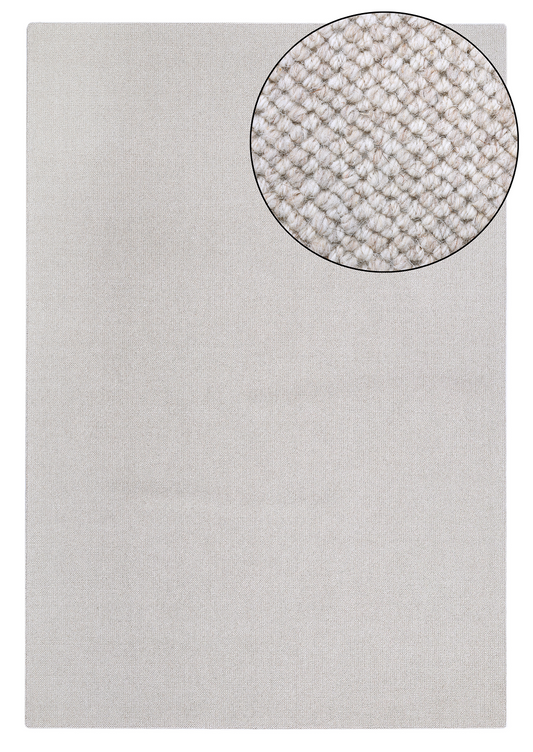
Creating textured yarns with varied tones involves several steps in spinning mills, combining fiber preparation, dyeing, and spinning techniques to achieve the desired appearance and texture. Here's a concise overview of the process:
Fiber Selection and Preparation: The process starts with selecting the raw fibers, often wool, cotton, or synthetic materials. The fibers are then cleaned, carded, and combed to
Blending: After dyeing, the fibers can be blended to create unique tonal variations. This step involves mixing different colors of fibers to achieve a specific look. The blend can range from subtle shifts in color to more distinct contrasts, depending on the spinning mill's design requirements.
Spinning: The spinning process involves twisting the fibers to form yarn. For textured yarns, mills might use different techniques to vary the tension, thickness, or twist direction, creating a textured effect. For example, slub yarns have intentional thick and thin sections, while boucle yarns incorporate loops to create a bumpy texture.
Texturing: In addition to traditional spinning methods, mills can use special machines or techniques to create additional texture. This might include air-jet texturing, where high-pressure air creates loops and curls in the yarn, or twisting and heat-setting to give the yarn a more complex structure.
Quality Control: Once the yarn is spun, it undergoes quality control to ensure consistent texture and color. Any irregularities or imperfections are addressed, and the yarn is prepared for further processing or distribution.
By combining these steps, spinning mills create textured yarns with varied tones that add depth, interest, and uniqueness to fabrics and textiles. These yarns are then used in weaving or knitting to produce products with distinctive visual and tactile appeal.